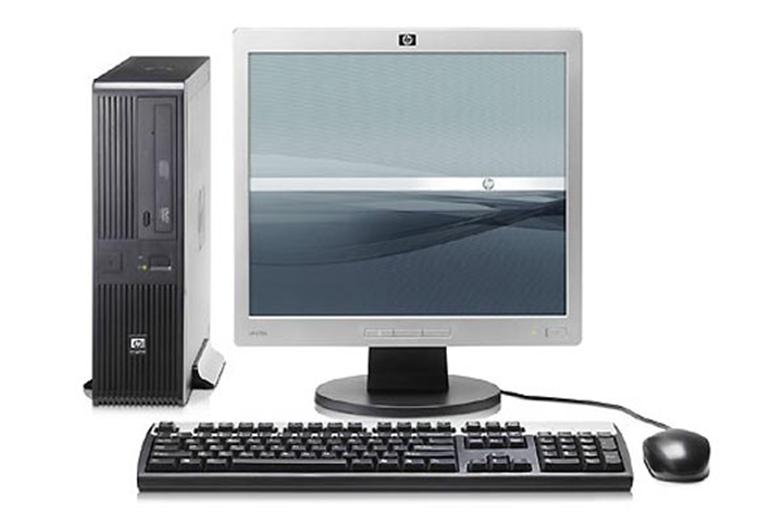
What is Personal Computer?: A personal computer (PC) is a general-purpose computer which is designed for personal uses. Its size, capabilities, and low cost make it useful for individuals. A personal computer may be a desktop, a laptop, tablet or a palmtop. It is based on microprocessor technology. Software applications! for personal computers include word processing, accounting, spreadsheet, databases, web browsers and e-mail, games and special-purpose software.
Modern personal computers often have high-speed or dial-up connections to the Internet, allowing access to the Internet and a wide range of other
resources. A PC may be used at home, or may be found in an office. Personal computers can be connected to a LAN (Local Area Network) either by a
cable or wireless.
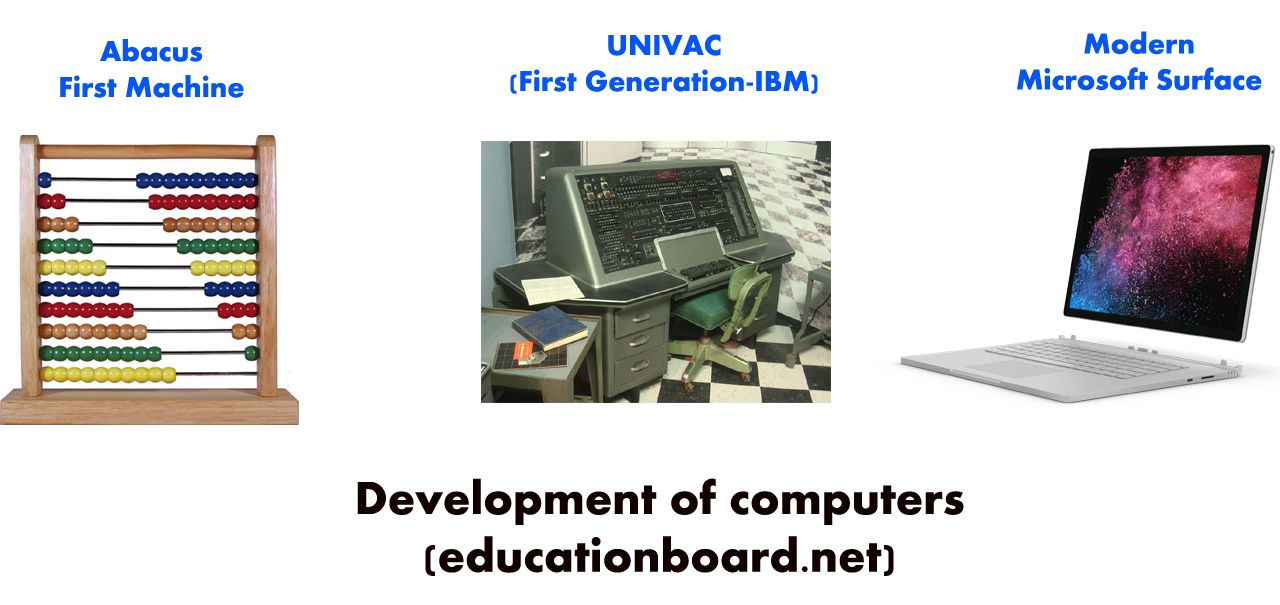
Development of Personal Computer
Personal Computers were made possible by two technical innovations in the field of microelectronics viz. the integrated circuit (IC), which was developed in 1959 and the microprocessor, which first appeared in 1971.
The IC permitted the miniaturization of computer-memory circuits, and the microprocessor reduced the size of a computer’s CPU to the size of a single silicon chip. The first complete personal computer was the Commodore PET introduced in January 1977. It was soon followed by the popular Apple II. In 1981, IBM (International Business Machine) introduced its own microcomputer model, the IBM PC. IBM PC was the most popular personal computer.
Parts of A Personal Computer
A personal computer isn’t a single part called the “computer.” A computer is a system that has many parts working together and each part has a special function.
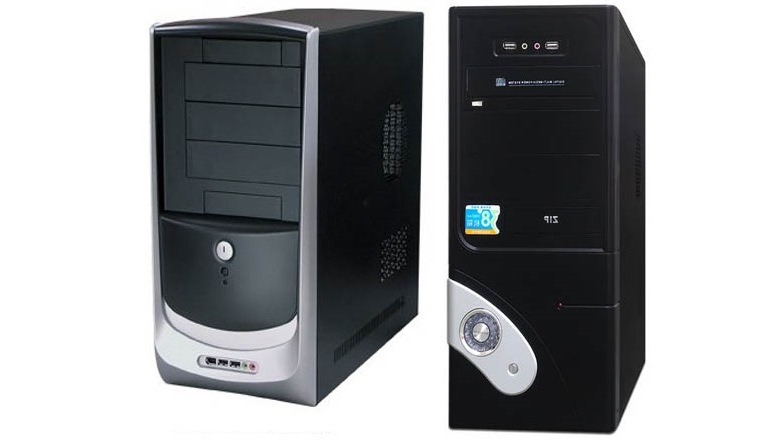
1. System Unit
The system unit is the main part of a computer system. It is a rectangular box placed on or under your desk that houses the important parts of a computer system. It includes the motherboard, microprocessor main memory, bus, and ports, but does not include the keyboard, monitor, or any peripheral devices.
Inside this box are the microprocessor, disc drives and other elements that work together to do the actual computing. The most important of these components is the central processing unit (CPU), or microprocessor, which acts as the “brain” of computer. Another component is random access memory (RAM), which temporarily stores information that the CPU uses while the computer is on. The information stored in RAM is erased when the computer is turned off.
All these functions are controlled by software which makes it possible for us to use computers. Almost every other part of computer such as keyboard, monitor, mouse and printer connects to the system unit using cables. The cables plug into specific ports, typically on the back of the system unit. Hardware that is not part of the system unit is sometimes called a peripheral device.
There are two types of system unit
- Desktop Type System unit : The desktop type system unit is a square box shaped structure which can lie flat on the desk or table and the monitor is usually placed on the system unit.
- Tower type System unit : This is another type of system unit. This type of system unit is vertically placed on the side of the monitor. The tower models are mostly used at homes and offices.
Main Parts of System Unit
(i) CPU
CPU is the most important part of a computer, where actual processing takes place. It is the brain behind all personal computers. It is also referred to as a processor or microprocessor.
Following are the various type of CPU chips:
- Pentium AMD
- Pentium Pro
- Pentium III
- Pentium IV
- Athlon
- Intel Celeron
- AMD Duron
- Cyrix
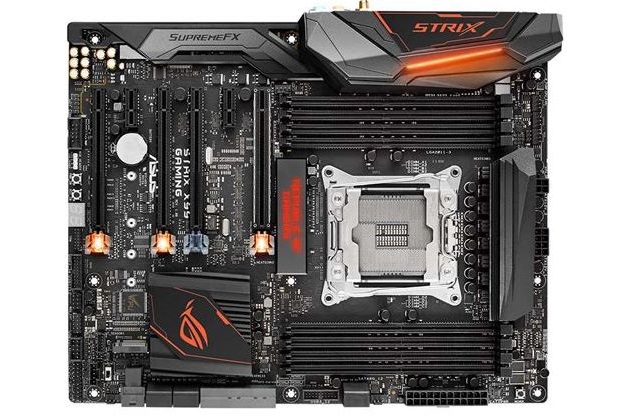
(ii) Motherboard
The motherboard is the flat circuit board on which fiber like structures of metal connecting pins are mounted. These metal connecting pins connect components to each other through which data, instruction and information are transferred. These fiber like structures of metal are called bus. The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer on which the processor, video card, sound card, IDE hard drive, etc. are all plugged into the various slots and connectors.
The CPU also plugs into the motherboard through a Socket or a Slot. On most computers, it is possible to add memory chips directly to the motherboard. We can also upgrade to a faster PC by replacing the CPU chip. To add additional core features, we may need to replace the motherboard entirely.
(iii) RAM
This is where our computer keeps the information it is using at the moment. RAM stands for Random Access Memory, and information is kept here only as long as it is needed by the application running on the Computer.
(iv) RAM Chip Slots
These slots are meant to expand the computer’s memory by adding RAM Chips.
(v) ROM
It is a silicon chip on motherboard on which instructions are burned at the time of manufacture. When computer is switched on, instruction stored is automatically initiated and after switching it off instructions do not get lost.
(vi) Math Co-processor Slot
Some Personal computers have a slot where Math Co- processor can be inserted. This processor assists the CPU in performing its mathematical operations.
(vii) Video Card
A video card is also called video adapter, graphics accelerator card, display adapter or graphics adapter or graphics card. lts function is to generate an output image to a display.
(vii) Sound Card
This card enables us to play sound and music. The sound card converts the digital information into electrical signals.
(ix) Power Supply
A power supply unit (PSU) is the component that supplies power to other components in a computer. A power supply unit is typically designed to convert AC from the mains to DC power for the different components of the computer. Most components require 5 volt while the floppy and hard disk require about 12 volts.
(x) Internal Speaker
It is a speaker on the computer motherboard that is responsible for beeps, beeping noises and other tones. This speaker is very basic and is not a speaker for playing songs, music, or other complex
sounds generated in a game.
(xi) Timer
It is an internal clock on the motherboard which is battery operated.
(xii) Expansion Slot
It is a long narrow connector which allow us to plug in expansion card like the sound card, network card etc. The primary purpose of an expansion card is to provide or expand on features not offered by the motherboard. The back side of system unit have ports and jacks to Connect different accessories. They are given below.
- Keyboard Port
- Serial Port
- Audio Jack
- Power Socket
- Monitor Port
- Parallel Port
- Network Port
- USB (Universal Serial Bus Port)
- SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) Port
2. Hard Disk
It is a hardware device which stores all Programs and data in the computer. So it is referred to as the memory bank of a computer. It is a permanent memory. So programs and data are not lost when the computer is turned off.
Larger the hard disk capacity, more the amount of programs and data that can be stored in it. In nearly all cases, it is permanently installed in the system unit and stores both the software the computer uses and the data files the user creates.
3. CD Drive
CD drive is a device that enables us to read and store the information on CD disks. It is usually located on the front of the system unit. CD drives use lasers to read data from a CD.
4. Floppy disk drive
Floppy disk drive is a device that enables us to read and store the information on floppy disks, also called floppies or diskettes. They also retrieve information more slowly and are more prone to damage.
5. Monitor
It is the part of the computer that looks like a small TV and shows you what is going on. Usually it has two cords, one for power and the other for connecting to the system unit. It displays text characters and graphics in gray shed or in colors.
6. Mouse
It is an input device and is used to point and select items on your computer screen.. By sliding the mouse around on a flat surface (usually on mouse pad) the user moves a pointer on the screen. When the tip of the pointer is positioned over the desired item, the user clicks the mouse (a single or double click) to select the item. A single cord connects the mouse to the system unit.
7. Key Board
It is a typewriter which contain keys to feed information into the computer. It is attached to the system unit with a cord. The standard and IBM keyboard have 83 keys but enhanced keyboard has 104 keys.
8. Speaker
It is an output device. When the speaker is connected to the sound card, the output as a sound can be heard on the speaker. Often it is used for entertainment.
10. Printer
It is an output device that produces print of images such as numbers, alphabets, graphs etc. on paper or hard-copy which is called printout.
11. Scanner
It is an input device that transfers typed or handwritten texts, graphs, diagrams and photographs to the computer in digital form.
12. CD-ROM Drive
CD-ROM drive is a device that reads the information stored on CD-ROM. CD-ROM is an abbreviated term for Compact Disks Kead Only Memory. The information stored in CD-ROM can neither be changed nor can new information be added to it.
13. CD-Writer
CD-Writer is a device that reads and writes information from CD.
14. Modem
It is a short form of Modulator-Demodulator. To connnect our computer to the Internet, we need a modem .A modem is a device sends and receives information over a telephone line or high-speed cable.
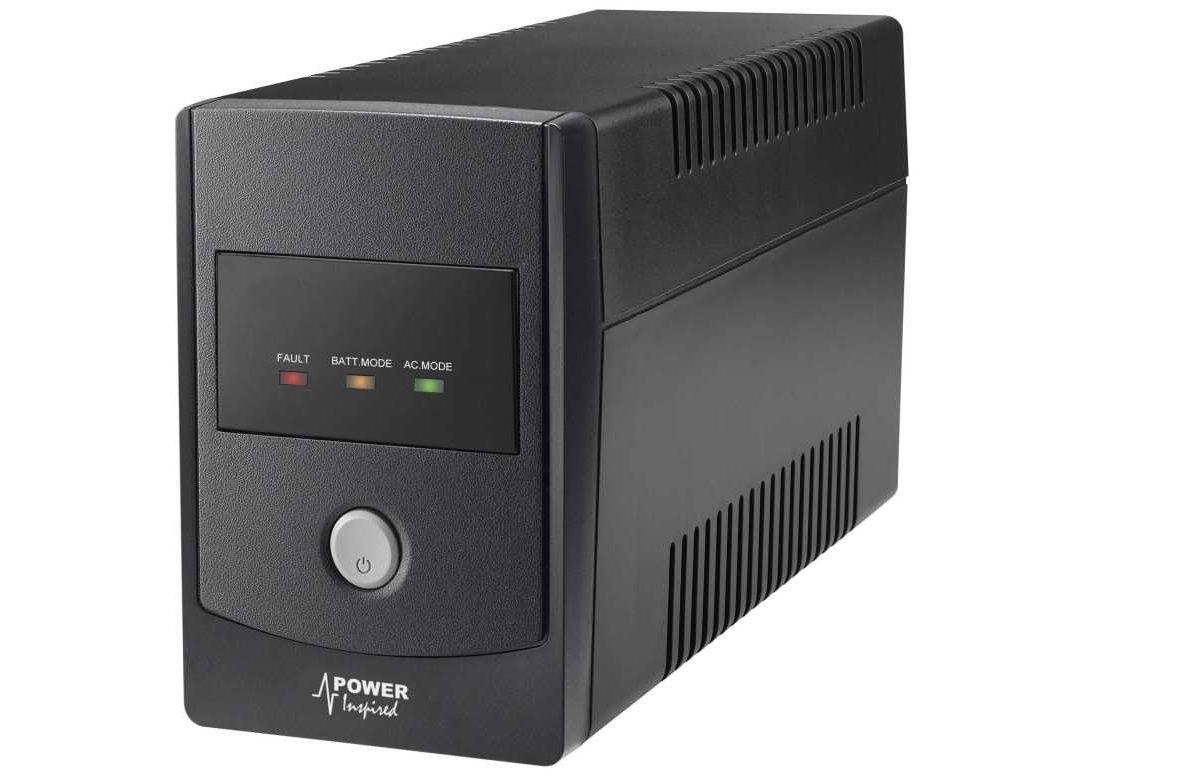
15. UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
Sudden power cut erases any present data. So a UPS can be used to provide uninterrupted power supply to the computer system and save the data typically for 5 to 15 minutes until an auxiliary power supply can be turned on and utility power restored, or equipment is safely shut down. It is also known as a battery backup.