Earth is a planet in the solar system. Earth has 2 types of movements:
-
Rotation or daily movement.
-
Revolution or annual movement.
1. ROTATION
Spins on its imaginary axis from west to east in 23 hrs, 56 min and 40.91 sec.
Rotational velocity at equator is 1667 km/h and it decreases towards the poles, where it is zero.
Earth’s rotation results in-
- causation of days and nights
- a difference of one hour between two meridians which are 15° apart;
- change in the direction of wind and Ocean currents
- rise and fall of tides every-day.
The longest day in North Hemisphere is June 21, while shortest day is on 22 Dec (Vice-versa in South Hemisphere).
Days and nights are almost equal at the equator.
2. REVOLUTION
Itis earth’s motion in elliptical orbit around the sun. Earth’s average orbital velocity is 29.79 km/s.
Takes 365 days, 5 hrs., 48 min and 45.51 sec. It results in one extra day every fourth year.
Revolution of the earth results in-
- change of seasons;
- variation in the lengths of days and nights at different times of the year;
- shifting of wind belts;
- determination of latitudes.
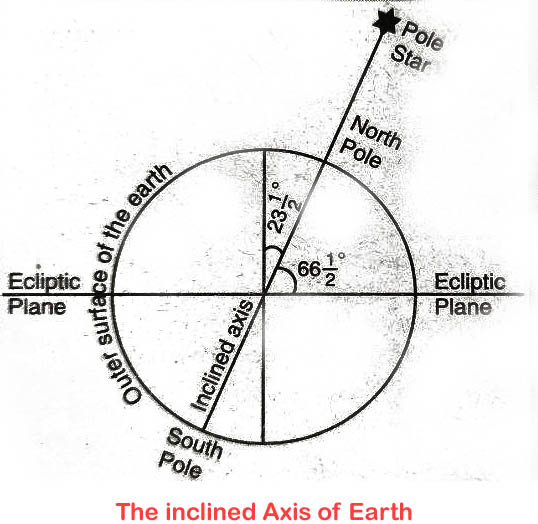
Inclined Axis
The axis is an imaginary line running from north to south and passing through the center of the earth. It always remains inclined at an angle of 661⁄2° to the plane of the earth’s orbit, and is tilted 231⁄2° from a line perpendicular to this plane.
The two facts, i.e., a fixed angle of the earth’s axis to the plane of the orbit and the axis always pointing in the same direction when combined with the earth’s movements, results in varying lengths of days and nights, seasonality and changes in the altitude of sun at different times of the year.
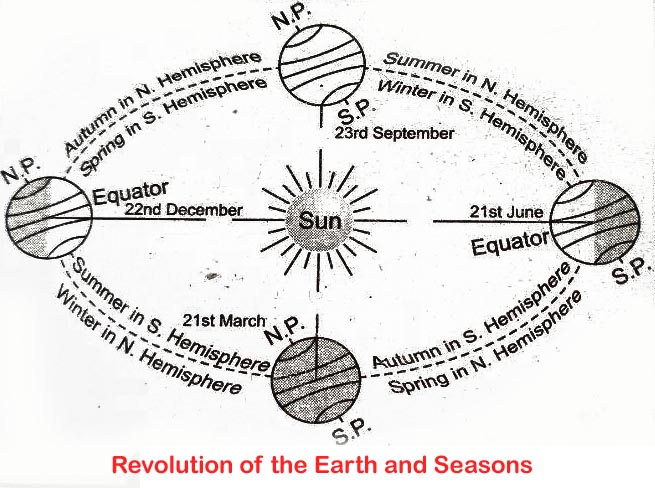
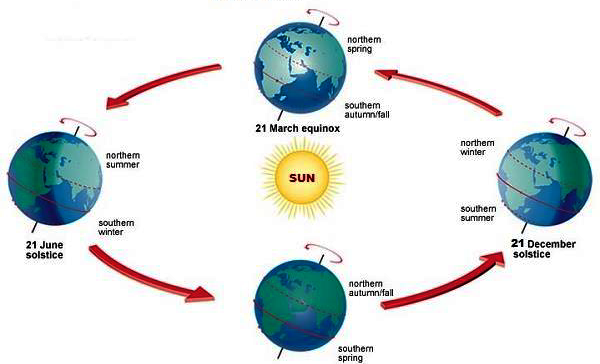
Seasons
Seasons are periods into which the year can be divided as a result of the climatic conditions, largely due to the changes in the duration and intensity of solar radiation.
The 4 seasons are:
1. Spring:
On March 21, the sun is directly overhead the equator. This is the season of spring in the northern hemisphere.
2. Summer
On June 21, the sun is directly overhead the Tropic of Cancer. Thus, the northern hemisphere experiences summer.
3. Autumn
On September 23, the sun returns to the equator, and the northern hemisphere experiences autumn.
4. Winter
On December 22, the sun is at the Tropic of Capricorn, and the northern hemisphere experiences winter.
EQUINOXES
These are dates when days and nights are equal. During these days the sun shines directly over the equator.
- March 21 – Vernal equinox
- September 23 – Autumnal equinox
SOLSTICE
The time of the year when the difference between the length of days and the length of nights is the largest. During these days the sun shines directly over the tropics.
- June 21 – Summer Solstice
- Dec 22 – Winter Solstice
MIDNIGHT SUN
It is a phenomenon, observable in the latitudes 661⁄2° North and South (or the Arctic and Antarctic Circles) where the sun does not sink below the horizon during summer.
This result due to the tilt of the earth’s axis, each hemisphere being inclined towards the sun during its summer. The duration of the phenomenon increases towards the poles, where it may be observed for six months of each year.
- North Pole experiences day from 21st March to 23rd September.
- South Pole experiences day from 23rd September to 21st March.
Some important facts about the Earth and its motions:
- The Earth has two speeds: rotation and rotation.
- Rotation is also called daily motion while revolution is called annual motion.
- Earth rotates from west to east on its axis, which is called the daily movement of the Earth.
- The Earth takes 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4.09 seconds to complete a rotation.
- Because of the daily movement of the Earth, only day and night occur.
- The earth revolves around its axis and revolves around the Sun, which is called annual motion.
- The Earth completes one orbit of the Sun in 365 days 6 hours 48 minutes and 45.51 seconds.
- The seasons change because of the annual motion of the Earth.
- The Earth’s axis tilts to 66.5 degrees from its orbit.
- Spring, summer, cold and rainy seasons come due to the tilted axis of the earth and the movement of the orbit.
- When the Earth is very close to the Sun, it is called Perihelion.
- Upsour status occurs on 3 January. On this day, the distance between the Earth and the Sun is 14.70 million km.
- When the Earth is at maximum distance from the Sun, it is called Aphelion.
- The condition of Apsour occurs on 4 July. In such a situation the distance between Earth and Sun is 15.21 million km.
- The line joining Upsaur and Apsaur passes through the center of the Sun. It is called apside line.



Earth spins around its axis, just as a top spins around its spindle. This spinning movement is called Earth's rotation. At the same time that the Earth spins on its axis, it also orbits, or revolves around the Sun. This movement is called revolution.